Category: Case Studies
Articles about two or more studies to explore a given topic.
Articles about two or more studies to explore a given topic.

Hospice fraud not only harms terminally ill patients but also devastates their caregivers and families. This article explores the impacts and offers tips on choosing a reliable hospice provider.

Navigating the complexities of end-of-life care can be challenging. This article delves into the nuances of terminal agitation and terminal restlessness, providing caregivers and family members with the essential knowledge to better understand and support their loved ones during the final stages of life.
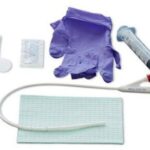
Discover the transformative role of Macy catheters in hospice and palliative care. This comprehensive guide explores how these innovative devices enhance patient comfort, simplify medication administration, and support caregivers. Learn about their benefits, proper use, and impact on the quality of life for those receiving end-of-life care.
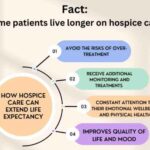
Hospice care not only provides comfort but can also extend the lives of terminally ill patients. Learn how holistic support and compassionate care improve longevity and quality of life.

Dive into hospice General Inpatient (GIP) care through real-life case studies. Discover how GIP can support patients with complex symptoms, learn about eligibility criteria, and understand why this valuable hospice benefit remains underutilized.

Discover how to revolutionize palliative care in nursing homes with our comprehensive guide. From staff training to pain management, learn about the latest approaches to ensure dignity and comfort for residents in their final stages of life. Explore practical solutions to common challenges and find out how to create a more compassionate care environment.

Explore why and when Hospice General Inpatient Care (GIP) is appropriate, Medicare compliance, eligibility, and what to do if a patient is ineligible.
Discover comprehensive strategies for preventing, detecting, and treating skin and soft tissue infections in the elderly. This guide covers critical aspects, including hygiene practices, early signs of infection, and effective treatment options.

Discover how hospitals are crucial in helping families place dementia patients in appropriate care settings. This article explores various care options, discusses challenges in placement decisions, and provides evidence-based strategies for effective hospital-based care coordination to ensure the best possible outcomes for patients and their loved ones.

Hospice care not only supports terminally ill patients but also plays a crucial role in reducing depression among caregivers and bereaved families. Discover how compassionate care and targeted interventions make a difference.

Learn about the diagnosis codes not allowed as primary diagnoses on hospice claims. This guide helps hospice agencies ensure accurate billing and optimal patient care.

Explore the powerful combination of hospice services and end-of-life doulas in providing holistic care for those facing terminal illness. Learn how these two approaches complement each other to support patients and families through the end-of-life journey.

Caring for terminally ill patients in denial can be challenging. This article explores why understanding denial is crucial and offers strategies for compassionate care. Techniques like Naomi Feil's validation therapy and motivational interviewing are highlighted to support patients respectfully, maintaining their dignity and emotional well-being.

Entering hospice care often means a terminal prognosis, but does it always mean death? This article delves into the purpose of hospice, the criteria for entering hospice care, and whether recovery is possible. Understand the nuances and what families and patients expect during this critical time.

Discover the transformative impact of music on dementia patients in this comprehensive guide. From improving cognitive function to enhancing mood and social engagement, music therapy offers a non-pharmacological approach to dementia care. Explore the science, benefits, and practical applications of integrating music into treatment plans for dementia patients.

Discover the critical role of trauma-informed care in hospice. This guide provides nurses and staff with the knowledge to support traumatized patients while educating caregivers and family members on providing empathetic end-of-life care.

Discover how acuity impacts hospice care. From assessment tools to real-world examples, this guide helps nurses and families navigate acuity levels.

Discover compassionate care techniques that address depression and anxiety in dementia without relying on antidepressants. This article delves into holistic approaches that enhance quality of life and promote mental well-being in dementia care.

Dive into the world of dementia diagnosis through MRI findings. This guide explores how different MRI indicators can hint at the type of dementia a patient might have. With real-life case studies, understand the importance of early detection and the future of MRI in dementia research.

This article delves into the transformative role of caregiver training in boosting Hospice CAHPS scores. Drawing on recent studies and expert insights, we explore practical strategies for enhancing caregiver education, ultimately leading to improved patient care and higher satisfaction ratings.
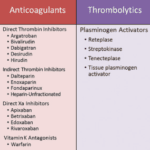
Anticoagulants can prevent blood clots but also cause bleeding risks for terminally ill patients. This article explains why these medications should be regularly reviewed for deprescribing, outlining factors like prognosis, preferences, and palliative care options to consider when making informed, compassionate choices aligned with the patient's goals.
A groundbreaking skin test has emerged as a potential game-changer in the early detection of Parkinson's disease and related disorders. This article explores the science behind the test, its accuracy, and the ethical implications of early diagnosis. Discover how this innovative approach could revolutionize Parkinson's treatment and patient care.

Discover how the GUIDE model can be applied in hospice and palliative care, offering improved support for dementia patients and their caregivers. Learn best practices and implementation strategies.
Hospice care is often misunderstood. A common myth suggests that once a patient with a terminal illness enters hospice, they lose control over their care. This article aims to dispel this misconception and highlight the central role of patient and family autonomy in hospice settings. It's important to note that this discussion primarily applies to patients receiving care at home or in non-facility settings, as facility-based patients may have less control over their care decisions.