Category: Tips For Nurses
Articles for nurses caring for terminally ill patients including how to manage challenging situations.
Articles for nurses caring for terminally ill patients including how to manage challenging situations.

Discover the potential side effects of dementia medications and how to support your loved one. Stay informed!

Discover gentle methods to encourage dementia patients to bathe. Learn how to create a positive bathing experience, use distraction techniques, and maintain a consistent routine. These compassionate approaches help caregivers navigate hygiene challenges while preserving dignity and reducing stress for both patient and caregiver.

Discover compassionate approaches to nourishing terminally ill loved ones. Learn about appetite changes, feeding techniques, and the importance of emotional support during meals. This guide offers practical tips for caregivers to ensure comfort and dignity while addressing nutritional needs in end-of-life care.
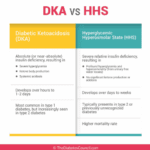
As an experienced hospice nurse, I understand that managing diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) and hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state (HHS) at end of life can be challenging, especially when patients choose to stop taking their diabetic medications or when those medications are no longer an option. In this article, I will provide information on recognizing the signs and symptoms of hyperglycemic crises and outline comfort-based treatment options that align with hospice goals of care.

Caring for a loved one with dementia can be challenging. One common struggle caregivers face is ensuring their loved one takes their medications. Dementia can make understanding and remembering medications difficult. In this guide, we'll explore effective strategies for encouraging your loved ones with dementia to take their medications, considering their unique needs.

I know that the journey you and your loved one are on can be challenging, especially when facing a terminal illness. As an experienced hospice nurse caring for terminally ill patients, I want to provide you with some valuable insights on a common issue that may arise during this time: contractures.
In this article, we will discuss how to use the Beers Criteria to identify PIMs and potential prescribing omissions (PPOs) in hospice patients. PPOs are medications that are indicated but not prescribed for a specific patient or population, or that are prescribed at a suboptimal dose or duration. We will also present 10 case studies to illustrate the medication reconciliation and deprescribing process and the outcomes of medication changes in different scenarios.

Caring for someone with dementia requires understanding and a heart full of compassion. This guide highlights the importance of patience and empathy and their profound impact on enhancing the lives of those with dementia.

Discover effective non-pharmacological methods to manage shortness of breath in hospice care. Learn about positioning techniques, breathing exercises, and environmental adjustments that can comfort and relieve patients experiencing dyspnea, enhancing their quality of life during end-of-life care.

Elopement is when a person with dementia leaves a safe area, like their home or care facility, without supervision. This can be intentional or unintentional, and it's important to address to ensure the safety of the patient. If your loved one is attempting to escape from a memory care facility, there are steps you can take to support both them and the facility.

This article will try to help you cope with this challenge. We will give you some information and advice on how to:
Prepare for the transition to a nursing home
Support your loved one during and after the move
Take care of yourself and your family.
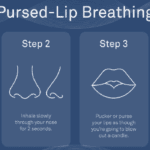
Dealing with shortness of breath can be challenging for terminally ill patients, but there are techniques that can help manage this symptom and improve their overall comfort. One such technique is pursed lip breathing. Pursed lip breathing is a simple and effective breathing technique that can help reduce shortness of breath and improve oxygen exchange in the lungs. As an experienced hospice nurse with years of experience, I will guide you through the steps of pursed lip breathing in a compassionate and easy-to-understand manner.
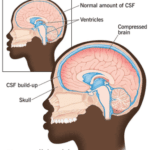
Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus (NPH) is a condition that occurs when cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) builds up inside the skull and presses on the brain. This can lead to various impairments in brain functions, such as thinking, memory, movement, and bladder control. NPH can also affect the quality of life, mood, and behavior of the person with NPH and their caregivers. The cause of NPH is often unknown, but it may be due to injury, bleeding, infection, brain tumor, or surgery on the brain. This article aims to provide a guide for families to understand NPH, its symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, and management, as well as how to cope with the challenges and uncertainties of living with NPH.

Navigating hospice eligibility for non-Alzheimer's dementia patients demands a personalized approach. Unlike Alzheimer's, there's no definitive scale, necessitating assessments of functional decline, mobility, communication, incontinence, weight loss, overall condition, and comorbidities. Effective documentation, clinical judgment, and compassionate care are crucial for supporting these patients and families.

Caring for a loved one with dementia can be both rewarding and challenging. If your loved one has been restless throughout their life, this restlessness may continue as a symptom of their dementia. As an experienced hospice nurse, I understand the difficulties you may face in managing habitual restlessness while ensuring the safety and welfare of your loved one. In this article, I'll provide you with practical tips and evidence-based practices to create a calming environment for your loved one, even if they have trouble with fine motor control due to arthritis or other factors.

This article will delve into common infections in geriatric patients, encompassing early, middle, and late-stage symptoms, preventive measures, and prevalent treatment approaches, particularly for patients facing a terminal illness prognosis of six months or less.

The purpose of this article is to provide you with some information and guidance about AAAs and how they can be managed in hospice patients.
Navigating the tender journey of hospice care, Compassion Crossing offers guidance on addressing the pivotal question of “when?”—a beacon for caregivers seeking solace and understanding in life’s final chapter.
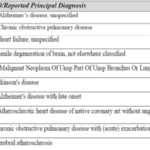
Explore the complexities of hospice care for terminally ill patients with multiple diagnoses. Learn how to distinguish between related and unrelated conditions, understand Medicare coverage, and navigate the challenges of providing comprehensive care while adhering to hospice regulations and ethical standards.

Identifying when a patient may benefit from hospice care is a critical yet often challenging task. For caregivers, including Certified Nursing Assistants (CNAs) and Medical Technicians (Med Techs), visual observation can be a powerful tool for recognizing signs that suggest a hospice referral might be appropriate.
This guide is tailored to assist caregivers in personal care facilities in identifying these signs through visual observation methods, helping provide compassionate and timely end-of-life care.

If you are caring for a terminally ill patient in hospice, you know how challenging it can be to manage their medications. You want to make sure they are getting the best possible care, but you also want to avoid unnecessary or harmful drugs that may worsen their quality of life or cause adverse effects.
That’s where medication reconciliation and deprescribing come in. Medication reconciliation is the process of reviewing and updating the patient’s medication list to ensure accuracy and completeness. Deprescribing is the process of reducing or stopping medications that are no longer needed, effective, or appropriate for the patient’s condition and goals of care.

This article provides hospice nurses with practical and evidence-based strategies to discuss end-of-life care with families
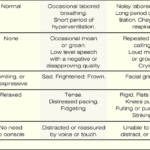
The PAINAD scale is a comprehensive tool that assesses and manages pain in older adults with dementia and delirium. It focuses on observable signs of pain rather than patient self-report, making it particularly useful for individuals who cannot communicate their discomfort
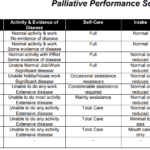
Explore the Palliative Performance Scale (PPS) and its crucial role in end-of-life care. Learn how this tool helps hospice professionals assess patient decline, predict life expectancy, and provide tailored care. Understand the significance of PPS changes in the final six months and how they guide compassionate care decisions.