Category: Assessment
Articles pertaining to nursing assessment often pertaining to terminally ill patients and recognizing key areas to prevent avoidable distress.
Articles pertaining to nursing assessment often pertaining to terminally ill patients and recognizing key areas to prevent avoidable distress.
As a hospice nurse, determining the appropriate frequency of scheduled nurse visits for your patients is essential to providing effective and compassionate end-of-life care. Patients and their families often rely on your expertise to ensure comfort and well-being during this sensitive time. In this article, we'll discuss suggested starting scheduled nurse visit frequencies, when to decrease or increase frequencies, and factors to consider based on patient acuity and changes in their condition.

Navigating hospice eligibility for non-Alzheimer's dementia patients demands a personalized approach. Unlike Alzheimer's, there's no definitive scale, necessitating assessments of functional decline, mobility, communication, incontinence, weight loss, overall condition, and comorbidities. Effective documentation, clinical judgment, and compassionate care are crucial for supporting these patients and families.
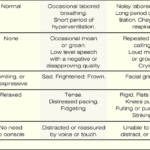
The PAINAD scale is a comprehensive tool that assesses and manages pain in older adults with dementia and delirium. It focuses on observable signs of pain rather than patient self-report, making it particularly useful for individuals who cannot communicate their discomfort
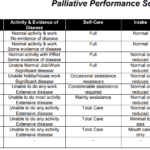
Explore the Palliative Performance Scale (PPS) and its crucial role in end-of-life care. Learn how this tool helps hospice professionals assess patient decline, predict life expectancy, and provide tailored care. Understand the significance of PPS changes in the final six months and how they guide compassionate care decisions.
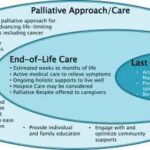
Explore the compassionate approach of hospice nursing assessments, emphasizing patient comfort and dignity over conventional hospital metrics. This article delves into the personalized care that defines hospice evaluations, ensuring a serene transition for patients and families.

Recognizing end-of-life signs can be challenging. This guide outlines key symptoms indicating a terminally ill patient may have less than two weeks, offering crucial insights for caregivers and families.
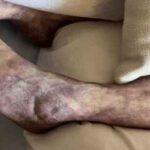
As a caregiver or family member, it can be challenging to witness the changes that occur as a loved one approaches the end of their life. One such change that may occur is mottled skin, also known as livedo reticularis. Understanding what mottled skin is and its significance in the dying process can help you provide the best care and support to your loved one during this time.

If you have a loved one with dementia, it can be difficult to know if they are in pain or discomfort. The Pain Assessment in Advanced Dementia Scale (PAINAD) is a tool that can help you determine if your loved one is uncomfortable. The Pain Assessment in Advanced Dementia Scale (PAINAD) is different from other pain assessment tools for people with dementia in several ways:

Heart failure is a complex medical condition that can impact the quality of life of patients, especially those in hospice care. As a hospice nurse, assessing the heart failure stage is crucial to providing appropriate care accurately. This article will explore the New York Heart Failure Classification System, its stages, and how to assess patients for their stages. Additionally, we will emphasize the importance of documentation in compliance with Medicare guidelines for terminally ill patients with heart failure.

Serotonin syndrome is a potentially life-threatening condition caused by an excess of serotonin in the body. Detecting this condition early is crucial, but it can be particularly challenging when dealing with dementia patients due to communication barriers and the complexity of their symptoms. In this article, we will present three case studies that highlight the early detection and successful management of serotonin syndrome in patients with different types of dementia: Alzheimer's disease, vascular dementia, and Lewy Body Dementia.

Hospice nurses assess the status of the patient's journey towards the end of life every nursing visit. Situations where a reversible condition can drastically impact the patient and the hospice assessment can occur. If it is not caught, it is potentially mistreated, leading to increased discomfort and a faster death, often involving increased suffering. One of the common clues that someone is getting closer to dying is increased agitation and restlessness.
Are you aware of Serotonin Syndrome?

Discover key indicators for end-of-life care in hospice. This guide highlights ‘trigger words’ that signal a patient’s final days, aiding nurses and caregivers in providing compassionate support during the most critical moments.

Dementia is a condition that affects millions of people worldwide, and it can cause a range of symptoms, including pain and discomfort. Unfortunately, pain is often under-detected and undertreated in people with dementia, leading to significant suffering and a reduced quality of life. In this article, we will explore the prevalence of pain among dementia patients, the impact of unmanaged pain on their quality of life, behavioral changes that may indicate pain, and the use of the PAINAD pain scale as a tool for assessing and managing pain in dementia patients.
It’s essential to familiarize yourself with the key local coverage determination (LCD) facts for different terminal illnesses to avoid admitting patients who are not eligible for services only to be required to refund the money back to Medicare; otherwise, only have the patient on for one benefit period then discharged for failure to decline. These determinations provide guidelines on the coverage of hospice services for specific conditions. If you are the admitting nurse, please do not just admit because you were told to admit by someone, regardless of the position or standing of the person or party that told you to admit. Use your critical thinking and clinical judgment skills to evaluate the patient for admission. Most doctors will write "evaluate and treat" or something to that effect; never lose sight of the "evaluate" portion of the doctor's order.
Based on the provided PDF files, as noted in the resources section below, let’s explore some essential information for each terminal illness.

Caring for a terminally ill loved one is a profound and challenging journey that requires compassion, understanding, and a willingness to alleviate any discomfort they may experience. In this guide, we will explore the concept of discomfort, its distinction from pain, and the importance of recognizing and addressing discomfort in addition to pain. You'll be better equipped to provide holistic care that enhances your loved one's quality of life during this sensitive time.
Throughout your loved one's illness, you might find yourself thinking that they don't require "pain medication" because they don't seem to be in pain. They might even respond with a direct "no" when asked about their pain. However, are you aware that most types of pain medication can alleviate discomfort? Did you also know that your loved one could be feeling uncomfortable without necessarily being in severe pain? Nonetheless, it's important to recognize that their discomfort requires the same treatment as if they were in pain.
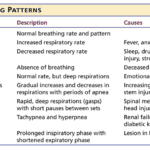
Understanding the final breath: This article explores the critical breathing patterns observed in the last hours of life, offering insights for caregivers and family members to prepare for the end-of-life journey.

It's common in nursing to be told by others that you shouldn't be a nurse, and some may even call you a "fake nurse" if you don't meet their standards of what they think is required to be a nurse. The first time I was told I could not be a nurse was by an elderly woman who believed only women could be nurses.

What does a typical day, a typical week look like for a visiting hospice registered nurse case manager look like?

One of the hardest portions of the job of a hospice nurse is to identify when a patient has two weeks of life left to live; this can be especially difficult at facilities going through staffing shortages leading to inconsistent caregivers with little to verbally report on a patient’s change of condition. Since being aware of the velocity of declines is extremely important, let’s cover an area that we in hospice (nurses, families, and caregivers alike) can keep an eye on in terms of identifying terminal restlessness which is often a key indicator for one week or less of life.

One of the most important roles is detecting and managing infections in terminally ill geriatric patients with dementia. These patients are often at higher risk for infections due to their weakened immune systems, underlying health conditions, and limited mobility. Detecting infections in these patients can be challenging due to their limited communication abilities and other cognitive and physical impairments. However, early detection and management of infections can significantly improve the patient’s quality of life and potentially prolong their life.
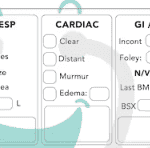
Hospice nurses play a vital role in providing quality care and comfort to terminally ill patients and their families. They must make accurate and timely assessments of the patient’s condition, needs, and preferences every visit. This article will outline the key aspects that hospice nurses should assess every visit, in addition to the standard physical assessment.

Recognizing the velocity of changes in a patient's condition is crucial for hospice nurses. By understanding the pace of changes in vital signs, symptoms, functionality, and more, nurses can anticipate needs, adjust care plans, and communicate the prognosis effectively with patients and families. The article provides guidelines on interpreting the velocity to estimate the time a patient has left.

This article offers guidance for new visiting hospice nurses struggling with work-life balance. It covers strategies like maintaining a recertification journal, pre-charting before visits, assessing end-of-life status, educating families, and preparing for a "good death." By following these tips, nurses can take less work home while delivering focused, compassionate care.
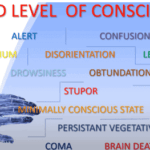
Understanding drowsiness, lethargy, and obtundation is crucial in hospice care. Drowsiness is a normal sleepiness, lethargy is more profound tiredness, and obtundation indicates severe unresponsiveness. Recognizing these levels helps in providing the right care and comfort for terminally ill patients.