Tag: Air Hunger
Articles about managing air hunger in the terminal ill.
Articles about managing air hunger in the terminal ill.

Discover effective strategies for managing end-of-life crises in hospice care. Learn how to recognize signs of distress, implement calming techniques, and provide compassionate support to patients and families. This guide offers practical tips for hospice nurses and caregivers to navigate challenging situations with confidence and empathy.

I have cared for many terminally ill patients over the years. One question that comes up frequently is should the dying patient be on oxygen at the end of life?
I see it from both sides, from hospice intake personnel as well as the admitting nurse — all had it drilled into them over the years that low oxygen saturation must be treated — to families who see how hospital and nursing home staff rush to put someone on oxygen because of low oxygen saturation.
Contrary to widespread belief, most dying patients do not need oxygen. Here’s why:

Guide to Recognize and Treat Common End of Life Symptoms provides tips on managing symptoms experienced by those at the end of their lives - Topics such as pain, shortness of breath, respiratory distress, and anxiety, and provides suggestions for medications and complementary therapies to help manage these symptoms.
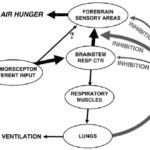
I can count the times I’ve run into air hunger at the end of life as a visiting RN Case Manager for going on five years on one hand. Over the years, I’ve managed patients with pulmonary fibrosis, lung cancers (diverse types), breast cancer, COPD, congestive heart failure, B-cell lymphoma, leukemia, and other diseases that can impact one person’s ability to breathe correctly. Air hunger is rare in my firsthand experiences, but it can happen.
Air hunger often sounds like the person is gasping for breath without regard to the actual respiratory rate (how fast they are breathing); it can also sound like stridor (YouTube videos below where you can hear the difference).