Category: About Hospice
Articles about hospice dispelling myths and bring more light to end-of-life topics.
Articles about hospice dispelling myths and bring more light to end-of-life topics.

Discover the true nature of hospice care in the U.S. This guide clarifies eligibility, focusing on comfort for those with a terminal prognosis of six months or less, and the support available for families and caregivers during this journey.

An article that guides families through understanding and exercising their rights to choose the best hospice care for their loved ones, ensuring their final chapter is written with compassion and respect.

Welcome to our guide on hospice care for undocumented immigrants. This article is crafted with the utmost empathy to support family members and caregivers as they navigate the complexities of end-of-life care. Our goal is to provide a clear understanding of hospice services and the unique challenges faced by undocumented immigrants during these tender moments.

In the world of healthcare, when a provider writes an order to "Eval and Treat" for hospice, they are asking for a thorough evaluation and a tailored treatment plan. This is specifically meant for patients who are being considered for hospice care. Let's delve into what this means and why it's crucial.
What Does "Eval and Treat" for Hospice Mean?

Caring for a loved one who has a terminal illness can be extremely rewarding but also particularly challenging. You may feel exhausted, overwhelmed, or isolated by the demands of caregiving. You may also feel guilty or anxious about taking a break from your loved one. But you deserve time to rest, recharge, and care for yourself. That is why hospice respite care can be a great option for you and your loved one.
Hospice respite care is a service that allows you to temporarily place your loved one in a facility, such as a hospital, nursing home, or hospice house, where they can receive professional care and support. You can use this time to do whatever you need or want, such as sleeping, working, running errands, visiting friends, or enjoying a hobby. Respite care can last up to five days at a time.

Discover how hospice patients can safely travel and create lasting memories with loved ones. Learn about essential preparations, medical considerations, and tips for a smooth journey. Explore ways to make the most of precious moments together while ensuring comfort and care during travel.

Discover the future of hospice care in 2024. This comprehensive guide explores cutting-edge pain management techniques, telemedicine integration, personalized care plans, and enhanced caregiver support. Learn how hospice services evolve to provide more compassionate and effective end-of-life care for patients and their families.

Caring for a terminally ill loved one is a challenging and emotional journey that requires strength, compassion, and support. As a hospice registered nurse case manager, I understand the importance of caring for patients, family members, and caregivers. In this article, we will explore the concept of respite care. This valuable resource offers rest and rejuvenation to caregivers while their loved ones receive specialized care in a skilled facility.
We will discuss respite care, its importance, Medicare coverage for respite care, the significance of skilled respite facilities, how often respite care can be provided, and tips for making respite care a positive experience for the caregiver and the loved one. Our goal is to empower patients, caregivers, and nurses by providing precise and concise information on this critical aspect of end-of-life care. Remember, you are not alone, and your love and dedication make a significant difference in the life of your terminally ill loved one.
Navigating the tender journey of hospice care, Compassion Crossing offers guidance on addressing the pivotal question of “when?”—a beacon for caregivers seeking solace and understanding in life’s final chapter.

Identifying when a patient may benefit from hospice care is a critical yet often challenging task. For caregivers, including Certified Nursing Assistants (CNAs) and Medical Technicians (Med Techs), visual observation can be a powerful tool for recognizing signs that suggest a hospice referral might be appropriate.
This guide is tailored to assist caregivers in personal care facilities in identifying these signs through visual observation methods, helping provide compassionate and timely end-of-life care.

Discover hospice care, eligibility, benefits, provider choice, costs, services, and more. Learn how hospice addresses physical, emotional, spiritual, and social needs and how to prepare for and manage them. Find out about the roles of the hospice team and the primary caregiver and the signs of approaching death. Empower yourself with the knowledge to make informed decisions about compassionate end-of-life care.
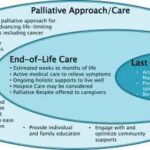
Explore the compassionate approach of hospice nursing assessments, emphasizing patient comfort and dignity over conventional hospital metrics. This article delves into the personalized care that defines hospice evaluations, ensuring a serene transition for patients and families.

Hospice volunteer coordinators ensure hospice patients receive the compassionate care and support they need during their end-of-life journey. In this article, we will explore the responsibilities of a hospice volunteer coordinator, address common misconceptions about hospice volunteers, and share insights from Hope Eberly, Volunteer Coordinator for Grane Hospice.

Deciding on end-of-life care for a loved one is challenging and emotional. One major decision to make is whether to opt for home hospice or hospice care at a facility. Both options have advantages and drawbacks, and understanding the pros and cons can help families make an informed choice. Here, we'll explore the pros and cons of each option and provide key questions that families should ask themselves to aid in their decision-making process.

This position involves being the first point of contact for families, patients, and facilities, making a lasting impression by offering both compassion and confidence in explaining hospice services. In this discussion, we will delve into the various aspects of the role of the Hospice Liaison, bringing insight from forever Christmas-loving Kathy Naccarato, including its dynamic nature, your dedication to dispelling misconceptions, and the importance of building relationships within the healthcare community.

Hospice care is often misunderstood and shrouded in myths that can prevent individuals and families from accessing the compassionate support they need during a challenging time. This article will address common misconceptions about hospice care and provide you with the facts. We aim to empower you with accurate information to make informed decisions when considering hospice for yourself or a loved one.

In this article, we will explore the vital role of a hospice chaplain, as explained by Katherine Seiler, an experienced and compassionate hospice chaplain. Hospice chaplains play a significant role in providing emotional, social, and spiritual support to terminally ill patients and their families during their end-of-life journey.

Hospice care is a vital form of healthcare dedicated to providing comfort and support to patients in their final stages of life. While it's a relatively recent concept in the United States, with its inception in 1974, it has gained significant popularity, with over half of Medicare beneficiaries in 2020 receiving hospice services. Nevertheless, as we delve into 2023, hospice care confronts several formidable challenges. These include labor shortages, concerns about the quality of care, and the notable presence of for-profit entities in the industry. In this article, we will navigate through the history of hospice care in the United States, its present state in 2023, and the challenges that affect not only hospice patients but also the dedicated staff and providers.
It’s essential to familiarize yourself with the key local coverage determination (LCD) facts for different terminal illnesses to avoid admitting patients who are not eligible for services only to be required to refund the money back to Medicare; otherwise, only have the patient on for one benefit period then discharged for failure to decline. These determinations provide guidelines on the coverage of hospice services for specific conditions. If you are the admitting nurse, please do not just admit because you were told to admit by someone, regardless of the position or standing of the person or party that told you to admit. Use your critical thinking and clinical judgment skills to evaluate the patient for admission. Most doctors will write "evaluate and treat" or something to that effect; never lose sight of the "evaluate" portion of the doctor's order.
Based on the provided PDF files, as noted in the resources section below, let’s explore some essential information for each terminal illness.

This article delves into hospice care with Andrew Viozzi, an adept hospice admission registered nurse. Andrew brings valuable insights into the hospice admission process and the broader spectrum of hospice care. Although Andrew's current position revolves around admissions, his extensive experience encompasses case management, preceptorship, mentorship, and the guidance of new hospice nurses. In this article, we dispel misconceptions, highlight the advantages of hospice care, outline the admission procedure, and emphasize the pivotal role of hospice in end-of-life care.

In the realm of hospice care, compassion and comfort take precedence. A team of skilled professionals comes together to offer comprehensive support to patients, their families, and caregivers. Among these essential contributors, Certified Nursing Assistants (CNAs) stand out as unsung heroes, bringing immeasurable value to the field of hospice care. This article delves into the distinctive role CNAs play in hospice, their frequent and meaningful interactions, and their leadership within the hospice team.

Is it Too Early to Start Hospice?
It's crucial to remember that hospice care is about improving the quality of life for the patient and their family, regardless of the time left. Hospice care can be initiated when the patient's condition is declining and they require comfort-focused care rather than life-prolonging treatments. Starting hospice care early can provide ample time for the patient and their family to benefit from the support and services offered.
If you're unsure when to consider hospice care, consult the patient's primary physician or a hospice care provider. They can guide you through the process and help you make an informed decision based on the patient's needs and circumstances.

Caring for a terminally ill loved one can be challenging. Still, with the proper support and understanding, you can help ensure they experience a comfortable and dignified end of life. Hospice care offers specialized medical and emotional support during this time. This guide aims to empower families new to hospice services by providing essential information on what to expect from a hospice provider and how to manage the journey towards a good death.

The longer I work in hospice, the more I'm reminded about two critical pieces of wisdom: 1) Hospice is about living, and 2) we should all do our best to live a life of least regrets.
While this article is geared towards family members with a terminally ill loved one, as well as my fellow workers in the fields of palliative and hospice care, I believe the thoughts that I will share apply to everyone alive near and far.