Safeguarding Seniors: A Comprehensive Guide to Respiratory Infections in the Elderly
Published on June 13, 2025
Updated on June 13, 2025
Published on June 13, 2025
Updated on June 13, 2025
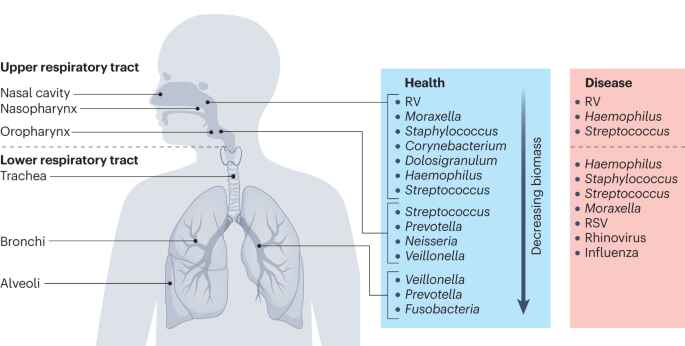
Table of Contents
Respiratory infections can be a severe concern for our elderly loved ones. Let’s explore what these infections are and why it’s crucial to understand and address them.
Respiratory infections are illnesses that affect the airways and lungs. In older adults, the two most common types are:
These infections can cause breathing difficulties, coughing, and other symptoms that can be particularly challenging for seniors.
Understanding and addressing respiratory infections in the elderly is vital for several reasons:
To better understand the differences between how respiratory infections affect younger adults versus older adults, consider this comparison:
| Aspect | Younger Adults | Older Adults |
|---|---|---|
| Immune response | Stronger, more effective | Weaker, less efficient |
| Symptom presentation | Typically clear and pronounced | Often subtle or atypical |
| Recovery time | Generally faster | Usually longer |
| Risk of complications | Lower | Higher |
| Impact on daily life | Less severe | More significant |
By recognizing the unique challenges respiratory infections pose to the elderly, we can take proactive steps to protect our loved ones and ensure they receive the care they need. In the following sections, we’ll explore prevention strategies, early detection methods, and treatment approaches tailored to the needs of older adults.
Remember, your attentiveness and care can have a significant impact on your elderly loved one’s health and well-being. Together, we can work towards keeping our seniors healthy and comfortable, even in the face of respiratory infections.
Understanding respiratory infections in older adults is essential for providing the best possible care. Let’s explore the common types, why our elderly loved ones are more vulnerable, and how these infections can present differently in seniors.
The two most prevalent respiratory infections affecting the elderly are:
Both of these can be serious, even life-threatening, for older adults. Let’s take a closer look at each:
Pneumonia is an infection that inflames the air sacs in the lungs. For seniors, it’s particularly concerning because:
While many view the flu as a common, less serious illness, it can be severe for seniors:
Our older loved ones are more vulnerable to respiratory infections for several reasons:
It’s essential to recognize that respiratory infections can manifest differently in seniors than in younger adults. Here’s a comparison:
| Symptom | Typical Presentation | Atypical Presentation in the Elderly |
|---|---|---|
| Fever | High temperature | May be absent or low-grade |
| Cough | Productive cough | It may be mild or absent |
| Chest pain | Present when breathing or coughing | It may be absent or mild |
| Fatigue | Present | This may be a primary symptom |
| Confusion | Not common | This may be a primary symptom |
| Appetite | Reduced | Severe loss of appetite |
| Falls | Not common | May increase in frequency |
In older adults, respiratory infections might manifest in unexpected ways:
It’s crucial to be vigilant and seek medical attention if you notice any of these changes in your elderly loved one, even if they don’t have typical respiratory symptoms.
Remember, early detection and treatment of respiratory infections can significantly improve outcomes for older adults. By understanding these infections and their unique presentations in the elderly, you can play a vital role in protecting your loved one’s health and well-being.
Protecting our elderly loved ones from respiratory infections is a team effort, and as caregivers and family members, we play a crucial role. Let’s explore some effective prevention strategies that can help keep our seniors healthy and safe.
Good hygiene is our first line of defense against respiratory infections. Here are some critical practices to encourage:
A healthy lifestyle can enhance the immune system and help protect against infections. Here are some tips:
Creating a healthy living environment is crucial. Consider these factors:
A well-nourished body is better equipped to fight off infections. Focus on:
Balanced diet: Encourage a diet rich in:
Hydration: Ensure your loved one drinks enough fluids throughout the day. Water, herbal teas, and clear soups are excellent choices.
Here’s a simple guide to help you remember key prevention strategies:
| Strategy | Why It’s Important | How to Implement |
|---|---|---|
| Hand Hygiene | Reduces transmission of germs | Frequent handwashing, use of hand sanitizers |
| Healthy Diet | Boosts immune system | Balanced meals with fruits, vegetables, and proteins |
| Hydration | Keeps airways moist, helps clear mucus | Offer water and other fluids regularly |
| Clean Environment | Reduces exposure to pathogens | Regular cleaning and disinfecting of living spaces |
| Physical Activity | Improves overall health and immunity | Encourage daily gentle exercises |
Remember, prevention is always better than a cure. By implementing these strategies, we can significantly reduce the risk of respiratory infections in our elderly loved ones. Your care and attention make a difference in keeping them healthy and happy. If you notice any signs of illness, please consult a healthcare professional without hesitation. Together, we can provide the best care possible for our seniors.
Early detection of respiratory infections in older adults is crucial for effective treatment and the prevention of complications. Your attentiveness as a caregiver and family member can make a significant difference. Let’s explore how to recognize warning signs, understand diagnostic challenges, and learn about essential check-ups and tests.
Respiratory infections in older adults may not always present with typical symptoms. Be alert for these potential warning signs:
Remember, any sudden change in your loved one’s behavior or health could be a sign of an infection. Trust your instincts if something seems off.
Diagnosing respiratory infections in seniors can be tricky for several reasons:
These challenges make it essential to work closely with healthcare providers and share any observed changes in your loved one’s condition.
Regular check-ups are vital for maintaining senior health and catching potential issues early. Here’s why they’re so important:
Aim to schedule check-ups at least once or twice a year, or more frequently if your healthcare provider recommends.
When a respiratory infection is suspected, healthcare providers may use various diagnostic tools and tests. Here’s a breakdown of common diagnostic methods:
| Diagnostic Tool/Test | What It Does | What to Expect |
|---|---|---|
| Physical Examination | Assesses overall health and listens to lung sounds | A painless imaging test requires standing still for a short time |
| Chest X-ray | Provides images of the lungs to detect inflammation or fluid | Blood draw from the arm may cause brief discomfort |
| Blood Tests | Checks for signs of infection and inflammation | Blood draw from the arm may cause brief discomfort |
| Pulse Oximetry | Measures oxygen levels in the blood | Painless clip placed on finger or earlobe |
| Sputum Culture | Analyzes mucus from the lungs to identify specific pathogens | Requires coughing up and spitting out mucus |
| Rapid Antigen Tests | Quickly detects specific viruses like influenza or RSV | Nasal or throat swab, results often available in minutes |
Your healthcare provider will determine the necessary tests based on symptoms and overall health status.
Remember, early detection is vital to managing respiratory infections in older adults. By staying vigilant, attending regular check-ups, and working closely with healthcare providers, you can help ensure your loved one receives timely and appropriate care. Don’t hesitate to contact medical professionals if you have any concerns – your observations and instincts are valuable in protecting your senior’s health.
As caregivers and family members, understanding the treatment approaches for respiratory infections in older adults is crucial. Let’s explore the various methods to help our loved ones recover, focusing on medical interventions and supportive care.
Non-pharmaceutical interventions are simple yet effective ways to help manage respiratory infections without the need for medication. These include:
Antiviral medications can be essential to treatment when influenza is diagnosed, especially for older adults. Here’s what you need to know:
| Antiviral | How It’s Taken | Common Side Effects |
|---|---|---|
| Oseltamivir | Oral capsule or liquid | Nausea, vomiting |
| Zanamivir | Inhaled powder | Bronchospasm (in some patients with respiratory conditions) |
| Baloxavir | Single-dose oral tablet | Diarrhea, bronchitis |
Antibiotics will be prescribed if your loved one is diagnosed with bacterial pneumonia. Here are some key points:
Alongside medical treatments, supportive care is essential for comfort and recovery:
Remember, every individual’s treatment plan may vary based on their specific condition, overall health, and the severity of the infection. Always follow your healthcare provider’s instructions, and don’t hesitate to ask questions or express any concerns.
Your role in providing care, comfort, and support is invaluable. By understanding these treatment approaches, you can better assist your loved one in recovery and ensure they receive the best care during this challenging time.
As caregivers and family members, understanding the potential complications and risk factors associated with respiratory infections in older adults is crucial. Let’s explore these essential aspects to help you provide the best care for your loved ones.
Respiratory infections can lead to severe complications in older adults. Here are some of the most common:
Certain factors increase the risk of older adults developing severe respiratory infections. Be especially vigilant if your loved one:
Proper management of existing health conditions is crucial in reducing the risk and severity of respiratory infections. Here are some strategies:
Here’s a table summarizing key risk factors and management strategies:
| Risk Factor | Management Strategy |
|---|---|
| Age (75+) | Regular health check-ups, vaccination |
| Chronic health conditions | Medication adherence, lifestyle modifications |
| Weakened immune system | Nutrition support, infection prevention measures |
| Smoking | Smoking cessation support |
| Living in care facilities | Enhanced hygiene practices, regular health monitoring |
Remember, early detection and prompt treatment are crucial in preventing complications. If you notice any changes in your loved one’s condition, such as increased confusion, difficulty breathing, or worsening symptoms, seek medical attention immediately.
Understanding these complications and risk factors and actively managing underlying health conditions can help protect your elderly loved one from severe respiratory infections. Your attentive care and support have a significant impact on their health and well-being.
As caregivers and healthcare providers, your role in supporting elderly patients with respiratory infections is invaluable. Explore effective care strategies to ensure the best possible outcomes for your loved ones or patients.
A safe environment is crucial for recovery and prevention of further complications. Here are some critical steps to create a safe space:
Careful monitoring and thorough documentation are essential for tracking the patient’s progress and communicating with the healthcare team. Here’s what to focus on:
Use a simple chart like this to keep track of important information:
| Date/Time | Temperature | Pulse | Breathing Rate | Blood Pressure | Symptoms | Medications Given | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Effective communication with healthcare providers is crucial for optimal care. Here are some tips:
Emotional Support for Patients
Emotional well-being is a crucial part of recovery. Here are ways to provide emotional support:
Remember, your presence and care have a significant impact on the patient’s recovery journey. You provide invaluable care by creating a safe environment, carefully monitoring and documenting their condition, communicating effectively with healthcare providers, and offering emotional support.
Remember to take care of yourself as well. Caregiving can be challenging, so take breaks, seek support when needed, and maintain your health. Your well-being is vital for you and for providing the best care to your loved one or patient.
Understanding the recovery and rehabilitation process for older adults after a respiratory infection is essential for caregivers and family members. Let’s delve into post-infection care, rebuilding strength and immunity, and managing long-term effects.
After a respiratory infection, older adults often need time and support to recover fully. Here are some critical aspects of post-infection care:
Rest and Hydration:
Medication Adherence:
Follow-Up Appointments:
Nutrition:
Monitoring Symptoms:
Rebuilding strength and boosting immunity are crucial for preventing future infections. Here are some strategies:
Physical Exercise:
Healthy Diet:
Adequate Sleep:
Stress Management:
Respiratory infections can have long-term effects, especially in older adults. Understanding and managing these effects is vital:
Chronic Respiratory Issues:
Weakened Immune System:
Reduced Physical Strength:
Mental Health:
Here’s a table summarizing key aspects of recovery and rehabilitation:
| Aspect | Key Points |
|---|---|
| Rest and Hydration | Ensure plenty of rest and fluids |
| Medication Adherence | Follow prescribed medication schedules |
| Follow-Up Appointments | Schedule and attend follow-up visits |
| Nutrition | Provide a balanced diet with nutrient-dense foods |
| Physical Exercise | Encourage gentle, regular exercise |
| Healthy Diet | Focus on foods high in vitamins and antioxidants |
| Adequate Sleep | Ensure 7-9 hours of quality sleep |
| Stress Management | Engage in relaxing activities and social interactions |
| Chronic Respiratory Issues | Monitor breathing difficulties and use prescribed treatments |
| Weakened Immune System | Support immune health with diet, exercise, and hygiene |
| Reduced Physical Strength | Encourage physical therapy and use assistive devices if needed |
| Mental Health | Provide emotional support and seek professional help if necessary |
By understanding these aspects of recovery and rehabilitation, you can provide comprehensive care for your elderly loved one. Your support and attention are crucial in helping them regain their strength and maintain their health. Remember, taking care of yourself is just as important, so ensure you also have the support you need.
As we conclude our discussion on respiratory infections in the elderly, let’s review the key points we’ve covered and emphasize the importance of proactive care. Your role as a caregiver or family member is invaluable in maintaining the respiratory health of your loved ones.
Let’s review the essential aspects we’ve discussed:
Understanding Respiratory Infections:
Prevention Strategies:
Early Detection:
Treatment Approaches:
Complications and Risk Factors:
Care Strategies:
Recovery and Rehabilitation:
Proactive care is crucial in maintaining the respiratory health of our elderly loved ones. Here’s why it matters so much:
Here’s a table summarizing the benefits of proactive care:
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Reduced Risk | Lowers the likelihood of contracting respiratory infections |
| Better Outcomes | Early detection and treatment lead to improved recovery |
| Improved Quality of Life | Maintains independence and overall well-being |
| Fewer Complications | Prevents serious health issues related to respiratory infections |
| Informed Decision-Making | Empowers seniors and caregivers with knowledge |
Remember, your attentiveness and care make a world of difference. By staying informed, vigilant, and proactive, you provide the best support for your elderly loved one’s respiratory health.
Caring for an elderly person’s respiratory health can be challenging, but it’s also enriching. Your efforts in prevention, early detection, and supportive care are invaluable. Don’t forget to take care of yourself, too – your well-being is just as important.
I appreciate your dedication to your loved one’s health. With your support and the information in this guide, you’re well-equipped to help maintain and improve your respiratory health. Remember, you’re not alone in this journey – don’t hesitate to contact healthcare professionals or support groups when you need assistance or advice.
Stay vigilant, stay informed, and continue to provide compassionate care for your elderly loved ones.
What to Know About Pneumonia in Older People
Difference Between Upper and Lower Respiratory Tract Infections
Preventing Respiratory Illness: Keeping Seniors Safe in Cold Weather
Supportive and palliative care for people with chronic respiratory disease and frailty
The potential of palliative care for patients with respiratory diseases
Bacterial Pneumonia in Older Adults
5 Common Lung Infections that Affect the Elderly
Articles on Advance Directives
CaringInfo – Caregiver support and much more!
The Hospice Care Plan (guide) and The Hospice Care Plan (video series)
Surviving Caregiving with Dignity, Love, and Kindness
Caregivers.com | Simplifying the Search for In-Home Care
Geri-Gadgets – Washable, sensory tools that calm, focus, and connect—at any age, in any setting
Healing Through Grief and Loss: A Christian Journey of Integration and Recovery
📚 This site uses Amazon Associate links, which means I earn a small commission when you purchase books or products through these links—at no extra cost to you. These earnings help me keep this website running and free from advertisements, so I can continue providing helpful articles and resources at no charge.
💝 If you don’t see anything you need today but still want to support this work, you can buy me a cup of coffee or tea. Every bit of support helps me continue writing and sharing resources for families during difficult times. 💙
VSED Support: What Friends and Family Need to Know
Take Back Your Life: A Caregiver’s Guide to Finding Freedom in the Midst of Overwhelm
The Conscious Caregiver: A Mindful Approach to Caring for Your Loved One Without Losing Yourself
Everything Happens for a Reason: And Other Lies I’ve Loved
Final Gifts: Understanding the Special Awareness, Needs, and Communications of the Dying
Top 30 FAQs About Hospice: Everything You Need to Know
Understanding Hospice Care: Is it Too Early to Start Hospice?
What’s the process of getting your loved one on hospice service?
Picking a hospice agency to provide hospice services
National Hospice Locator and Medicare Hospice Compare
Bridges to Eternity: The Compassionate Death Doula Path book series:
Additional Books for End-of-Life Doulas
VSED Support: What Friends and Family Need to Know
Find an End-of-Life Doula
At present, no official organization oversees end-of-life doulas (EOLDs). Remember that some EOLDs listed in directories may no longer be practicing, so it’s important to verify their current status.
End-of-Life Doula Schools
The following are end-of-life (aka death doula) schools for those interested in becoming an end-of-life doula:
The International End-of-Life Doula Association (INELDA)
University of Vermont. End-of-Life Doula School
Kacie Gikonyo’s Death Doula School
Laurel Nicholson’s Faith-Based End-of-Life Doula School
National End-of-Life Doula Alliance (NEDA) – not a school, but does offer a path to certification
Remember that there is currently no official accrediting body for end-of-life doula programs. It’s advisable to conduct discovery sessions with any doula school you’re considering—whether or not it’s listed here—to verify that it meets your needs. Also, ask questions and contact references, such as former students, to assess whether the school offered a solid foundation for launching your own death doula practice.