Introduction to Adult Failure to Thrive
Adult Failure to Thrive is a condition that affects older adults. Understanding what it is and why recognizing and addressing it matters is essential.
What Is Adult Failure to Thrive?
Adult Failure to Thrive refers to a decline in an older person’s overall well-being. It’s not just about physical health; it encompasses emotional, social, and functional aspects. Imagine a gradual loss of vitality, like a wilting flower. Adult Failure to Thrive involves:
- Weight Loss: Significant weight loss (more than 5% of baseline) often results in the diagnosis of Protein Calorie Malnutrition.
- Decreased Appetite: A reduced desire to eat.
- Poor Nutrition: Inadequate intake of essential nutrients.
- Inactivity: A decline in physical activity and engagement.
Why Is Recognizing Adult Failure to Thrive Important?
- Multifactorial Causes: Adult Failure to Thrive isn’t caused by a single factor. Chronic diseases, functional limitations, and psychosocial factors all play a role. Recognizing it early allows us to address these underlying issues.
- Predictive of Adverse Outcomes: Adult Failure to Thrive is associated with negative outcomes, such as infections, impaired immunity, hip fractures, and even mortality.
- Quality of Life: By identifying Adult Failure to Thrive, we can intervene to improve overall quality of life and prevent needless suffering.
Overview of Main Topics Covered in the Article
- Causes and Risk Factors: We’ll explore the various factors contributing to Adult Failure to Thrive, including chronic diseases, medications, and social isolation.
- Assessment and Diagnosis: How do we recognize Adult Failure to Thrive? We’ll discuss physical and psychosocial assessments, lab tests, and medication reviews.
- Interventions: What can we do? We’ll focus on treatable causes—nutrition, physical activity, and addressing chronic conditions.
- End-of-Life Discussions: Adult Failure to Thrive prompts conversations about end-of-life care. We’ll emphasize compassionate discussions and avoiding unnecessary interventions.
Intended Audience
This guide is for family members and caregivers who support older adults. Whether you’re a concerned relative or a dedicated caregiver, understanding Adult Failure to Thrive empowers you to make informed decisions and provide compassionate care.
Remember, recognizing Adult Failure to Thrive is pivotal in an elderly person’s journey. Let’s approach it with empathy and a commitment to their well-being.
What is Adult Failure to Thrive?
Adult Failure to Thrive is a condition that affects older adults. It’s essential to recognize its signs and take action. Here’s what you need to know:
What Is Adult Failure to Thrive?
Adult Failure to Thrive is like a fading sunset—a gradual decline in both physical and mental well-being. Imagine a loved one losing their sparkle, their energy waning. It’s not just about the body; it’s about the spirit, too. Adult Failure to Thrive involves:
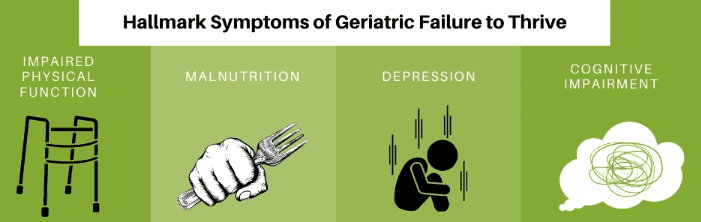
- Physical Decline: Weight loss, weakness, and fatigue.
- Emotional Strain: Low mood, sadness, and social withdrawal.
- Cognitive Changes: Confusion, forgetfulness, and difficulty concentrating.
Common Causes of Adult Failure to Thrive
- Chronic Diseases: Conditions like heart disease, diabetes, or chronic lung problems can sap vitality.
- Social Isolation: Loneliness takes a toll—when connections fade, so does resilience.
- Depression: The weight of sadness affects both body and mind.
- Cognitive Impairment: Dementia clouds memories and decision-making.
- Malnutrition: Poor eating habits lead to weakness and vulnerability.
- Dehydration: Lack of fluids affects energy levels.
- Infections: Repeated infections drain vitality.
- Medication Side Effects: Some drugs can unintentionally sap strength.
Observable Symptoms
- Weight Loss: Clothes hanging loose, belts tightened.
- Weakness: Struggling with everyday tasks.
- Fatigue: Feeling tired all the time.
- Poor Appetite: Food losing its appeal.
- Low Mood: A heaviness in the heart.
- Confusion: Misplacing keys, forgetting names.
Why Addressing Adult Failure to Thrive Matters
- Quality of Life: Recognizing Adult Failure to Thrive allows us to intervene and improve daily life.
- Preventing Complications: Adult Failure to Thrive can lead to infections, falls, and hospitalizations.
- Compassionate Care: We can provide empathy and support by understanding Adult Failure to Thrive.
How to Care for Loved Ones with Adult Failure to Thrive
- Physical Well-Being:
- Nutrition: Ensure balanced meals. Monitor food intake and encourage small, frequent meals. Include protein, fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
- Hydration: Remind them to drink water regularly. Dehydration worsens Adult Failure to Thrive symptoms.
- Pain Management: Address discomfort promptly. Consult their doctor for pain relief options.
- Emotional Support:
- Listen Actively: Be present. Let them express their feelings without judgment.
- Validation: Acknowledge their emotions. Adult Failure to Thrive can be isolating; your empathy matters.
- Companionship: Spend quality time together. Share stories, laughter, and memories.
- Social Interaction:
- Engage: Encourage visits from friends and family. Social connections combat loneliness.
- Activities: Plan outings or hobbies they enjoy. Attend community events together.
- Spiritual Needs:
- Comfort: Respect their beliefs. Spiritual practices can provide solace.
- Reflection: Encourage moments of quiet reflection or prayer.
Consulting with Health Care Team
- Regular Check-Ins: Keep their doctor informed about any changes. Regular visits are crucial.
- Medication Review: Ensure they take prescribed medications correctly. Discuss side effects.
- Professional Help: Seek guidance from nurses, social workers, or hospice services when needed.
Remember, your compassion and attentiveness make a significant difference.
When to Consider Hospice for Adult Failure to Thrive
What Is Hospice?
Hospice is a specialized form of care that enhances the quality of life for individuals with serious illnesses. It provides comprehensive support to patients and their families during the final stages of life. Rather than focusing solely on curative treatments, hospice emphasizes comfort, pain management, emotional well-being, and dignity.
How Can Hospice Benefit Adult Failure to Thrive Patients and Their Families?
Hospice care offers several benefits for Adult Failure to Thrive patients and their families:
- Comfort and Symptom Management: Hospice professionals work closely with patients to manage pain, fatigue, and shortness of breath symptoms. They prioritize the patient’s comfort and overall well-being.
- Emotional and Spiritual Support: Hospice provides counseling and emotional support to patients and their families. Trained professionals help address fears, anxiety, and emotional distress during this challenging time.
- Family Education and Guidance: Hospice teams educate family members about the disease process, what to expect, and how to provide care. They offer guidance on practical matters, including caregiving techniques and emotional coping strategies.
- Bereavement Support: Hospice extends support to families even after the patient’s passing. Bereavement services help family members navigate grief and loss.
Indicators for Considering Hospice
While Adult Failure to Thrive itself is not a specific diagnosis for hospice admission, certain indicators suggest that hospice may be appropriate:
- Advanced Stage of Illness: When the patient’s condition has progressed significantly, curative treatments are no longer effective.
- Poor Prognosis: If the physician predicts a life expectancy of six months or less due to the natural course of the disease.
- Limited Treatment Options: When treatments have been exhausted or are ineffective.
- Frequent Hospitalizations: If the patient experiences recurrent hospitalizations due to complications related to AFTT.
Enrolling in Hospice
Please note that Medicare now generally considers adult failure to thrive under the broader category of protein-calorie malnutrition.
- Physician Evaluation: The patient’s primary care physician or specialist assesses their condition and determines hospice eligibility based on the earlier criteria.
- Patient and Family Decision: The patient and their family choose hospice care, opting for comfort-focused support over curative treatments.
- Hospice Admission: Once eligible, the patient is admitted to hospice. The hospice team develops an individualized care plan that addresses physical, emotional, and spiritual needs.
- Services Provided by Hospice:
- Palliative Care: Focusing on symptom management and pain relief.
- Emotional Support: Counseling and assistance with emotional distress.
- Bereavement Support: Offering guidance to family members during and after the patient’s passing.
Remember that hospice care aims to enhance the patient’s quality of life and provide compassionate support to patients and their families during this challenging journey.
Caregiver Support Resources
Caring for a loved one with an Adult Failure to Thrive can be emotionally and physically demanding. Acknowledging the unique stressors you face is crucial. Here are some common challenges:
- Emotional Strain: A decline in your loved one’s health can evoke sadness, frustration, and helplessness.
- Physical Demands: Providing daily care, managing medications, and assisting with daily activities can be exhausting.
- Social Isolation: Caregiving often limits social interactions, leading to feelings of loneliness.
- Financial Stress: Balancing caregiving responsibilities with work and financial obligations can be overwhelming.
Information and Education
- Alzheimer’s Association: Their website provides valuable information on Adult Failure to Thrive, caregiving tips, and resources.
- UpToDate: A trusted medical resource with articles on Adult Failure to Thrive management and treatment.
- MSD Manual: Offers comprehensive information on caring for older adults, including Adult Failure to Thrive.
Emotional and Social Support
- Support Groups: Connect with other caregivers facing similar challenges. Sharing experiences can provide comfort and practical advice.
- Online Forums: Websites like Caregiver Action Network (caregiveraction.org) offer forums where you can ask questions and find support.
- Respite Care: Arrange for short breaks from caregiving. Respite services allow you to recharge and take care of your own needs.
Practical Support
- Local Agencies: Contact your local Area Agency on Aging or Aging and Disability Resource Center. They can guide you to community resources.
- Family and Friends: Reach out to your support network. Delegate tasks and ask for help when needed.
- Financial Assistance: Explore programs that offer financial aid for caregivers.
Remember, you are not alone. Seeking support and taking care of yourself are essential for providing the best care to your loved one.
Conclusion
In this guide, we’ve explored the complexities of caring for loved ones with Adult Failure to Thrive. As family members and caregivers, your unwavering dedication is admirable and impactful. Let’s recap the essential points:
- Understanding Adult Failure to Thrive:
- Adult Failure to Thrive involves a gradual decline in physical and emotional well-being.
- It’s not just about weight loss; it encompasses social isolation, emotional strain, and cognitive changes.
- Why Recognizing Adult Failure to Thrive Matters:
- Early recognition allows for timely interventions.
- Adult Failure to Thrive predicts adverse outcomes and affects overall quality of life.
- Holistic Care:
- Attend to physical needs (nutrition, hydration, pain management).
- Provide emotional support (active listening, companionship).
- Encourage social interaction and engage in meaningful activities.
- Consulting with Health Care Team:
- Regular check-ins with the doctor are crucial.
- Medication reviews and professional guidance are essential.
Key Takeaways for Caregivers
- Self-Care Matters: Remember to care for yourself too. You’re an essential part of the equation.
- Seek Support: Reach out to support groups, online forums, and local agencies.
- Celebrate Small Victories: Every moment of connection and comfort matters.
A Grateful Note
To all caregivers, we extend our heartfelt gratitude. Your compassion, resilience, and unwavering commitment make a profound difference in the lives of those you care for. You are not alone on this journey. Together, we can provide comfort, love, and hope.
Resources
Failure to Thrive in Older Adults – What You Need to Know
Failure to Thrive in Elderly Adults: Diagnosis & Treatment
Thriving Through the Years: Overcoming Failure to Thrive in Aging Adults
50+ Failure To Thrive Elderly Life Expectancy Statistics
Top 30 FAQs About Hospice: Everything You Need to Know
Understanding Hospice Care: Is it Too Early to Start Hospice?
What’s the process of getting your loved one on hospice service?
Picking a hospice agency to provide hospice services
National Hospice Locator and Medicare Hospice Compare
The National Academy of Elder Law Attorneys (NAELA) is dedicated to improving the quality of legal services provided to older adults and people with disabilities
Articles on Advance Directives
Eldercare Locator: a nationwide service that connects older Americans and their caregivers with trustworthy local support resources
CaringInfo – Caregiver support and much more!
The Hospice Care Plan (guide) and The Hospice Care Plan (video series)
Surviving Caregiving with Dignity, Love, and Kindness
Caregivers.com | Simplifying the Search for In-Home Care
Geri-Gadgets – Washable, sensory tools that calm, focus, and connect—at any age, in any setting
Healing Through Grief and Loss: A Christian Journey of Integration and Recovery
📚 This site uses Amazon Associate links, which means I earn a small commission when you purchase books or products through these links—at no extra cost to you. These earnings help me keep this website running and free from advertisements, so I can continue providing helpful articles and resources at no charge.
💝 If you don’t see anything you need today but still want to support this work, you can buy me a cup of coffee or tea. Every bit of support helps me continue writing and sharing resources for families during difficult times. 💙
Caregiver Support Book Series
VSED Support: What Friends and Family Need to Know
My Aging Parent Needs Help!: 7-Step Guide to Caregiving with No Regrets, More Compassion, and Going from Overwhelmed to Organized [Includes Tips for Caregiver Burnout]
Take Back Your Life: A Caregiver’s Guide to Finding Freedom in the Midst of Overwhelm
The Conscious Caregiver: A Mindful Approach to Caring for Your Loved One Without Losing Yourself
Dear Caregiver, It’s Your Life Too: 71 Self-Care Tips To Manage Stress, Avoid Burnout, And Find Joy Again While Caring For A Loved One
Everything Happens for a Reason: And Other Lies I’ve Loved
The Art of Dying
Final Gifts: Understanding the Special Awareness, Needs, and Communications of the Dying
How to read and apply the FAST Scale to stage any type of dementia. Dementia Staging Made Easy
📚 This site uses Amazon Associate links, which means I earn a small commission when you purchase books or products through these links—at no extra cost to you. These earnings help me keep this website running and free from advertisements, so I can continue providing helpful articles and resources at no charge.
💝 If you don’t see anything you need today but still want to support this work, you can buy me a cup of coffee or tea. Every bit of support helps me continue writing and sharing resources for families during difficult times. 💙
The 36-Hour Day: A Family Guide to Caring for People Who Have Alzheimer’s Disease and Other Dementias
Creating Moments of Joy Along the Alzheimer’s Journey: A Guide for Families and Caregivers, Fifth Edition, Revised and Expanded
Geri-Gadgets – Washable, sensory tools that calm, focus, and connect—at any age, in any setting
Caregiver Support Book Series
Dementia Caregiver Essentials: Comprehensive Guide for Dementia Care (one book that contains the ten books below for less than one-third the price of all ten)
The Validation Breakthrough: Simple Techniques for Communicating with People with ‘Alzheimer’s-Type Dementia’
Dementia Home Care: How to Prepare Before, During, and After
DEMENTIA DENIED: One Woman’s True Story of Surviving a Terminal Diagnosis & Reclaiming Her Life
Atypical Dementias: Understanding Mid-Life Language, Visual, Behavioral, and Cognitive Changes
The Dementia Caregiver’s Survival Guide: An 11-Step Plan to Understand the Disease and How To Cope with Financial Challenges, Patient Aggression, and Depression Without Guilt, Overwhelm, or Burnout
Fading Reflection: Understanding the complexities of Dementia
Dementia Caregiving: A Self Help Book for Dementia Caregivers Offering Practical Coping Strategies and Support to Overcome Burnout, Increase Awareness, and Build Mental & Emotional Resilience
Navigating the Dementia Journey: A Compassionate Guide to Understanding, Supporting, and Living With Dementia
Ahead of Dementia: A Real-World, Upfront, Straightforward, Step-by-Step Guide for Family Caregivers
Four Common Mistakes by Caregivers of Loved Ones with Dementia and What Do Differently (video)
My Loved One with Dementia
How to read and apply the FAST Scale to stage any type of dementia. Dementia Staging Made Easy. (Video)
Understanding Dementia (Alzheimer’s & Vascular & Frontotemporal & Lewy Body Dementia) (Video)
How Do I Know Which Dementia I’m Looking At? (Video)
Geri-Gadgets – Washable, sensory tools that calm, focus, and connect—at any age, in any setting
Dementia Training material (Free)
Promoting Meaningful Relationships with Dementia Patients through Validation Therapy
Unlocking the Power of Validation Therapy in Compassionate End-of-Life Care
Validation Therapy: A Valuable Tool for Families and Healthcare Teams
Best Practices for Approaching Combative Dementia Patients
Dementia Insights: The Validation Method for Dementia Care
The Validation Breakthrough: Simple Techniques for Communicating with People with Alzheimer’s Disease and Other Dementias
How Do I Know You? Dementia at the End of Life
The Dementia Caregiver: A Guide to Caring for Someone with Alzheimer’s Disease and Other Neurocognitive Disorders (Guides to Caregiving)
Sundown Dementia, Vascular Dementia and Lewy Body Dementia Explained
The Caregiver’s Guide to Dementia: Practical Advice for Caring for Yourself and Your Loved One (Caregiver’s Guides)
Ahead of Dementia: A Real-World, Upfront, Straightforward, Step-by-Step Guide for Family Caregivers
The Dementia Caregiver’s Survival Guide: An 11-Step Plan to Understand the Disease and How To Cope with Financial Challenges, Patient Aggression, and Depression Without Guilt, Overwhelm, or Burnout
Dementia Care Companion: The Complete Handbook of Practical Care from Early to Late Stage